Featured Article:State Building in Somalia in the Image of Somaliland: A Bottom-Up Approach
By
2014, Vol. 6 No. 03 | pg. 1/4 | »
IN THIS ARTICLE
AbstractThe creation of western-style government institutions has been unsuccessful in Somalia. This is a direct result of colonial administrations not laying the proper foundation for western government institutions to achieve legitimacy in a culture of clan and kinship based identity. In post conflict Somalia the top down approach to state building has been ineffective and a lack of government structure at the time of independence created an environment in which clan based fracturing of the government was inevitable. The existing clan and kinship examples of local governance replaced the central government starting in 1991 when the Somali state collapsed. Since then several examples of a bottom up approach to state building have emerged throughout Somalia. These attempts at state building have been quite successful and should be reviewed as a means for successful state creation in greater Somalia. Somaliland’s attempts at state building have proven to be comparatively successful and should be viewed as a model for successful state creation in third world or tribal type states. According to the Failed States Index compiled by the Fund for Peace and Foreign Policy, Somalia has been the number one failed state in the world since 2008. The 2011 Ibrahim Index of African Governance rates Somalia an 8 out of 100, making it a state “with no ability to create or implement policies that promote the well-being of people within its borders” (Gordon & Gordon, 2012, p.103). There have been at least sixteen attempts since 1991 to reconstitute the failed Republic of Somalia (Walls, 2009, p.372). During this time no single representative government controlled the entire territory of Somalia or even maintained a prolonged existence. Southern Somalia, the area formerly known as Italian Somaliland, is claimed by several groups, none of which maintains control over more than a few square miles, and in the case of the internationally recognized Transitional National Government (TNG) and its successor, the Transitional Federal Government (TFG), only a few blocks of the capital Mogadishu have been successfully controlled (Anonymous, 2002, p.259; Menkhaus, 2006 p.92). For twenty-two years Somalia has been a black hole of government, international aid and efforts at state and nation building. Attempts by the international community to stabilize Somalia have been many, with billions in international aid poured into the region, yet tangible results have been virtually nonexistent. However, there is an example of successful state building within Somalia: the stable yet unrecognized Somaliland Republic in northwestern Somalia.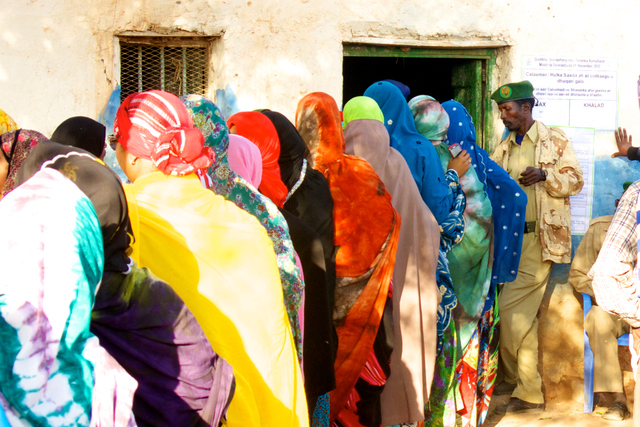  Somaliland's example provides the most compelling alternative to the failed attempts to implement governance in Somalia from above. Here, voters line up prior to the opening of polls in November 2012 elections that were predominantly peaceful. Photo: Dustin Turin.
Somaliland's example provides the most compelling alternative to the failed attempts to implement governance in Somalia from above. Here, voters line up prior to the opening of polls in November 2012 elections that were predominantly peaceful. Photo: Dustin Turin.
Western government models have repeatedly failed in Somalia. Multiple internationally supported transitional governments have been unable to take control of the country’s territory and repeated foreign interventions have done little to provide stability. These top-down approaches to government formation are based on the western assumption that Somalia as a whole is a failed state based on a Westphalian model. According to Max Byrne this narrative of a failed state “occludes the reality of the situation and is harmful to attempt to encourage development from within the country” (2013, p.113). "For many Somalis, the state is an instrument of accumulation and domination, enriching and empowering those who control it and exploiting and harassing the rest of the population" (Menkhaus, 2006, p. 87). The success story in neighboring Somaliland, which has led to a locally legitimate and organically grown government, has largely been ignored by international actors. In states with little or no functioning government there is “evidence that social and political structures are characterized by ‘hybrid political orders’ which blend ‘traditional and modern norms and practices’” (Debiel, Glassner, Schetter & Terlinden, 2009, p.38). Somaliland has used traditional practices to create a sustainable modern government by blending “modernity and tradition” (Jhazbhay, 2009, p.51) into a functioning state. A Failed Historical LegacyDuring colonial rule the Italian and British administrators did not create the necessary institutional foundation for a strong central government. Once independence and unification were achieved in 1960 the resulting government was unable to consolidate its position. Moreover, the decentralized clan and sub-clan pastoral system that defines Somali culture can be seen as fundamentally contrary to a centrally organized state: “During unification very little thought was apparently given, either by enthused Somali nationalists or their international supporters, as to whether the European-style centralized state that was hastily created was necessarily appropriate for the diffuse nature of Somali society” (Pham, 2012, p.10). Due to an exclusion of traditional clan-based governance structures the Somali unification experiment was predestined to fail. Meanwhile, the local stability of clan and sub-clan structures in Somalia have made top-down implementation of western-style governance excessively difficult. The inability to form a viable government over the past two decades has earned Somalia the “dubious distinction of being the world’s foremost graveyard of externally sponsored state-building initiatives” (Menkhaus, 2006, p.74).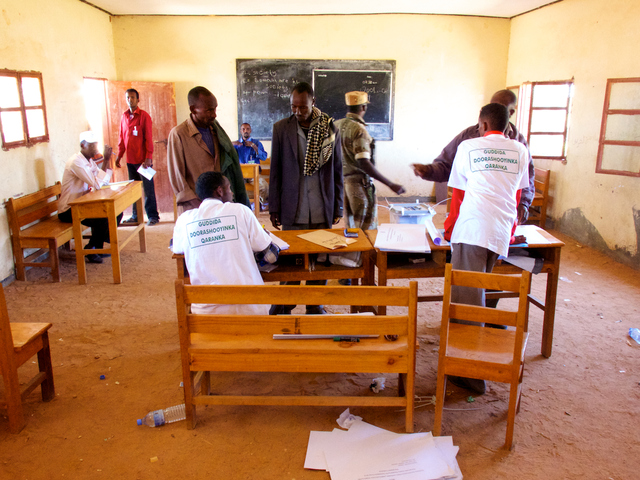 
Multiple nationwide elections have taken place with relative peace and calm in Somaliland. Above, a quiet polling station near Salaxley, Somaliland during November 2012 elections. Photo: Dustin Turin. Although it lacks international recognition, Somaliland is the lone example of a functioning sovereign state in the Horn. The unrecognized state of Somaliland “has now functioned since 1991 as a self-sustaining state and has repeatedly received positive attention from the international media for the way it has embarked upon post-conflict reconstruction” (Doornbos, 2002, p.95). This is largely due to the bottom up approach at state building that derives its legitimacy from local clan elders and the local ownership of civil institutions, including stable economic, political, security and social welfare institutions. Compared to international attempts at imposing western style government on Somalia, “the Somaliland ‘nation-building’ process was more bottom-up and does function as a state” (Kibble, 2001, p.18). The methods for state formation in Somaliland may provide the best model for stabilization efforts in greater Somalia: at this point, “it is clear that development in Somalia must focus on bottom-up, organic growth rather than [the] imposition of institutions” from above (Byrne, 2013, p.122).Continued on Next Page » Suggested Reading from Inquiries Journal
Inquiries Journal provides undergraduate and graduate students around the world a platform for the wide dissemination of academic work over a range of core disciplines. Representing the work of students from hundreds of institutions around the globe, Inquiries Journal's large database of academic articles is completely free. Learn more | Blog | Submit Latest in Political Science |